Over the past three decades, Passivhaus has become established as the world’s most rigorous energy efficiency standard, reducing carbon emissions, and cutting heating consumption by up to 60-80%. Passivhaus will play a crucial role in achieving net zero carbon targets with its emphasis on energy performance, occupant comfort, and sustainability.
The Core Principles of Passivhaus
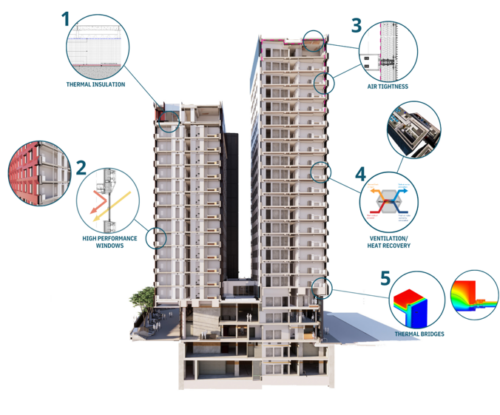
To earn Passivhaus certification, a building must adhere to the five key principles of Passivhaus:
- Exceptionally High Levels of Insulation: High-quality insulation is essential to maintain a stable indoor temperature, minimising the need for additional heating or cooling.
- Well-Insulated, Triple-Glazed Windows: These windows prevent heat loss while allowing natural light to penetrate, improving both energy efficiency and indoor comfort.
- Thermal Bridge-Free Design and Construction: Passivhaus buildings avoid unwanted heat loss or gain by eliminating thermal bridges, ensuring a consistent indoor environment.
- Airtight Building Envelope: A tight building envelope prevents drafts and energy loss, enhancing overall efficiency.
- Ventilation with Highly Efficient Heat Recovery: Advanced ventilation systems recover heat from exhaust air, ensuring a fresh air supply without significant energy loss.
Passivhaus Building
Why Passivhaus Matters
Energy Efficiency: Passivhaus buildings use significantly less energy compared to conventional buildings, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and lowering utility bills for occupants.
Occupant Comfort: Passivhaus standards ensure a comfortable living environment with consistent temperatures, good air quality, and reduced noise pollution. This is achieved through meticulous design and the use of high-performance materials and systems.
Sustainability: By prioritising energy efficiency and the use of sustainable materials, Passivhaus contributes to a more sustainable built environment.
Long-Term Value: Buildings constructed to Passivhaus standards often have higher long-term value due to their reduced operating costs, increased durability, and lower environmental footprint.
Passivhaus in Practice
Adopting Passivhaus principles involves:
- Advanced Insulation Techniques: Ensuring buildings are insulated to the highest standards.
- High-Performance Windows: Utilising triple-glazed windows to maximise energy efficiency and comfort.
- Eliminating Thermal Bridges: Designing and constructing buildings to prevent any unwanted heat loss or gain.
- Airtight Construction: Ensuring building envelopes are meticulously designed to be airtight, preventing energy loss.
- Efficient Ventilation Systems: Using innovative ventilation systems to recover heat and provide fresh air without significant energy loss.
These principles are being applied in various sectors, including residential, commercial, and public buildings, demonstrating the versatility and effectiveness of Passivhaus design.
The Future of Passivhaus
As the demand for sustainable and energy-efficient buildings continues to grow, the adoption of Passivhaus principles is expected to increase. Governments and organisations worldwide are recognising the benefits of Passivhaus and are incorporating these standards into building regulations and policies.
Passivhaus is more than just a building standard; it is a commitment to a sustainable future. It embodies the principles of efficiency, comfort, and sustainability that are essential for the buildings of tomorrow. By adopting Passivhaus standards, we can create energy-efficient, comfortable, and sustainable living and working spaces that contribute to a healthier planet.
Passivhaus matters because it addresses the urgent need for energy efficiency and sustainability in the built environment. Its rigorous standards ensure that buildings are not only comfortable and cost-effective but also environmentally responsible. By embracing Passivhaus, we are taking a significant step towards a more sustainable and resilient future.










